Great people management skills allow leaders to drive the best outcomes for the company, resolving conflicts, finding optimal solutions to problems, and enhancing employee performance.
This guide covers the ten people management skills every manager needs, from how to lead teams to effective decision-making and multitasking.

What are people management skills?
People management skills are typically defined as “soft skills” that allow managers to communicate and lead individuals and teams to deliver the best results. Great people management begins with the company culture and continues throughout the work experience, emboldening staff with clear and consistent communication about their roles and responsibilities.
This guide will help you to supercharge your people management skills, exploring the techniques and digital tools to transform your leaders. Covering the ten strong people management skills every manager needs, these resources will help foster leaders capable of improving employee motivation and career development.
Why do we need people management skills?
People management skills offer business leaders the means to create fully functional workforces capable of becoming star players. Managers who are capable of leading by example can model the best possible behaviours so that employees know exactly what standards are expected from them.
In their article on the pros and cons of people management, Gallup outlines five core traits that every great manager should embody. These traits are:
1. Motivation
Perhaps the most important trait of all is motivation, i.e. the ability to get individuals and teams to work hard and perform their roles to a high standard. Great managers energise their teams and create an innate sense of enthusiasm and pride in accomplishments.
2. Workstyle
Managers also need to excel with day-to-day goal setting while providing access to the necessary resources to get the job done. This can be achieved through the use of performance management software to set and track objectives and key results (OKRs) and other metrics for goals.
3. Initiation
Tied into motivation, initiation means influencing others to act decisively and tackle adversity head-on. This means not only facilitating the relevant tools and resources but also fostering a positive mindset that is capable of overcoming resistance.
4. Collaboration
Managers are often responsible for complex teams made up of people with varying skill sets. They are expected to strengthen bonds between employees and their colleagues with a commitment to success.
5. Thought process
Great managers exhibit an analytical thought process capable of effective decision-making, often while under pressure. This requires a multi-variant approach to strategising so that different outcomes can be gamed through.
Understanding and applying these skills can make the difference between success and failure. When implemented correctly, these management skills can increase productivity and create a more engaged and motivated workforce. They also give employees the confidence to act decisively and solve problems without needing constant guidance.
10 people management skills you need
Let’s take a closer look at ten people management skills you need to consider, and the tools and processes available to help put these into action.
Team-building skills
Team building is a people management skill that requires managers to establish clear tasks across multiple dimensions so that each team member has their work correctly coordinated. This means sharing high-level goals over long-time scales, breaking them down into their core components that can be tracked on a day-to-day basis.
Great team-building also means empowering team members to define their tasks collectively with an understanding of each team member’s particular skill set. When done correctly, managers can avoid micromanagement and allow teams to get to work and deliver results on time and to a high standard.

Leadership skills
It goes without saying that leadership skills are central to great management. Leading individuals and teams to success require a series of core abilities to motivate and engage employees to deliver their best performance.
The report from Deloitte, The changing role of people management in the digital age, outlines some of the core leadership skills necessary to meet contemporary workplace challenges. These include:
- Adaptability: Each individual has their own style of working, so effective leaders should allow people the appropriate scope and freedom to innovate.
- Tolerance: Encourage experimentation and the development of ideas, with employee brainstorming sessions via digital platforms such as Microsoft Teams channels and company intranet groups.
- Mobility: Champion the use of digital tools and media, and enable flexible and contingent working hours. This means understanding how hybrid working patterns can be used to enhance flexibility while improving well-being.
- Leadership at all levels: Provide a degree of direction to employees by removing barriers to progress and enabling them to succeed. HR can help facilitate this process through a comprehensive system designed to facilitate succession planning and other leadership programs.
- Collaboration: Bring together different parties and people to leverage varied and diverse skill sets for collaboration and problem-solving. Understand how these skill sets can facilitate coaching and mentoring programs.
- Decision-making: Be able to make quick, analytics-based decisions. Develop the right team in place to deliver key insights when needed. This can be supported through the use of performance data and analytics reports.
- Communication: Be highly visible, and accessible and communicate frequently with colleagues across grades and levels, using a multi-channel communications platform for consistent messaging.
- Feedback: Provide real-time feedback and reward individual and team achievements, whether through casual verbal rewards or explicit recognition systems embedded in performance management software.

Negotiation and conflict resolution skills (Problem-solving skills)
People management requires the ability to deliver diplomacy and conflict resolution, negotiating a solution that is equitable for everyone involved. This means juggling different opinions and priorities while managing conflict in a way that delivers outcomes that benefit individuals and the company at large.
In order to achieve this, managers require a holistic understanding of the roles and responsibilities of all concerned parties so that conflict can be managed through reduction, avoidance, or elimination. Through an understanding of various perspectives, conflict can be avoided through accommodation and compromise, leading to positive outcomes for everyone involved.
Listening skills
One of the main problems with bad managers is their management style often has a tendency to dictate and delegate without being responsive to feedback. Great managers understand the importance of listening as much as talking. Hearing what employees have to say allows them to gain insights into any problems they’re facing, offering the best solutions possible.

Managers can achieve this by:
- Training themselves to be active listeners, giving employees their full attention
- Asking questions and seeking clarification
- Clarifying their understanding by summarising what they’ve heard back to their employee
- Offering potential solutions and advice in a way that encourages problem-solving
- Factoring in emotional intelligence with a conscious effort to consider the employee’s well-being
Communication skills
Just as great people management requires well-formed listening skills, so too does it encompass great communication skills. Managers need to be able to articulate themselves in a clear and concise manner so that people understand what is expected of them.
This can be facilitated through the use of a multi-channel communications system as part of performance management tools, ensuring the correct messaging reaches everyone it is intended for.
Multi-tasking skills
Multi-tasking is a foundational skill required from all managers, whether managing small teams on niche projects or large departments with hundreds of employees. This means being able to write out a comprehensive list of tasks which can then be prioritised on a daily basis.
Effective multi-tasking as a manager also means understanding when to delegate tasks, and which employees are the best candidate to get the desired results. Planning and scheduling regular one2one meetings with staff, chasing up any ongoing issues, and providing viable solutions also fall under the umbrella of multi-tasking skills.
Decision-making skills
Great managers are those capable of making difficult decisions under potentially extreme pressure. Decisions often need to be made from numerous variables, so good leaders need to be able to adapt and act decisively when the stakes are high.
There are many models managers can use as a guide for their decision-making process. One example is the DECIDE model, as outlined by the National Library of Medicine in the context of healthcare management.
This model encompasses six core activities for decision-making, each outlined as part of the DECIDE acronym.
- Define the problem
- Establish the criteria
- Consider all the alternatives
- Identify the best alternative
- Develop and implement a plan of action
- Evaluate and monitor the solution and feedback when it is necessary
These six steps help managers make decisions that are based on all the information available to them while being able to assess the impact of their decision and adjust actions where necessary.
Admin skills
While the HR department typically handles the day-to-day processing of human resources, people management skills for managers nevertheless involve many of their core skills. Managers frequently liaise with HR professionals throughout the course of their work, whether helping with onboarding new staff to dealing with performance-related issues.
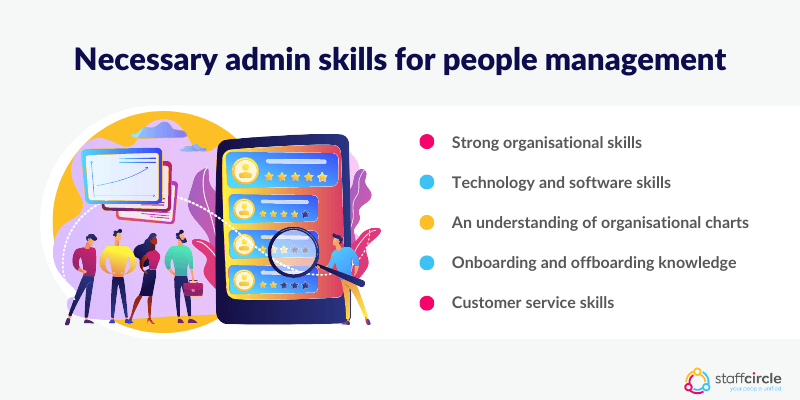
Some of the admin technical skills necessary for great people management include:
- Strong organisational skills for maintaining records, files, and information and data relevant to employee performance
- Technology and software skills, for example using HR employee analytics reports software to assess attendance and other HR-related areas that impact performance
- An understanding of departmental and organisational charts and other tools for assessing employee skill sets and training requirements
- Onboarding and offboarding processes, ranging from establishing Personal Development Plans (PDPs) to conducting exit interviews
- Customer service skills for when dealing with clients and customers
Motivation skills
Motivating and engaging employees within a team or department is another top priority for management. Motivated employees are ones who deliver their work on time and to the highest possible quality. Managers are expected to fulfil this sense of motivation, whether this is through intrinsic or extrinsic motivational mechanisms.
Extrinsic motivation is when managers determine the pay raise or bonus of an employee based on their performance. This can also include promotions, where they are rewarded for their work with a better position within the company.
Intrinsic motivation is intimately linked to an employee’s sense of professional development. Arguably of more value than extrinsic motivation, this can be integrated into the daily workflow, from a verbal “thank you” to rewards issues through recognition programs.
When a company adopts a rewards and recognition program, managers can make sure that this is instigated fairly. They can also pair individual rewards with team rewards, thus enhancing motivation at the group level. Instilling a healthy degree of competitiveness is another effective tool managers can use to improve the motivation and engagement of employees.
People skills
Managers are required to deal with a range of people each with their own skills and temperaments. To do this well, they need solid people skills and the ability to adapt depending on who they are dealing with. Great leaders inspire confidence in employees of all different backgrounds, helping to unlock their potential and build successful teams.
How people management skills can improve company culture
A company’s culture is strengthened in various ways when people management skills are successfully employed throughout the workplace. Here are a few ways company culture improves due to effective leadership.
Ability to motivate your employees
We’ve touched on motivation already, and this is something that can be interwoven into the company’s core cultural values. Motivation is an infectious quality, and when increasing numbers of employees become enthusiastic about their work it becomes easier to spread motivation to other employees.
When all managers within the company have the same skills and experience in improving employee motivation and performance, it becomes an intrinsic component of the culture.
Connecting and being accessible
Employers are increasingly concerned with the emotional and physical well-being of their employees. I order to do this, they need to demonstrate that they are available for conversations around sometimes sensitive matters, and have the employee’s best interests at heart.
Managers who are accessible and approachable and provide spaces for communication help foster a culture of trust through strong relationships. A culture that values these conversations doesn’t just benefit from greater attention to well-being issues, it also encourages brainstorming and lateral thinking.
Showcasing empathy
The ability to show empathy often ties into being accessible, giving employees the confidence that any issues they have will be dealt with appropriately. It can be easy for managers to miss the nuances around issues of poor performance, so practising empathy helps create mindfulness around problem-solving and diplomacy.
Decisiveness
Great leaders need to make clear-cut decisions at short notice, often with potential downsides if the wrong decision is made. This means they need to be decisive, capable of trusting their own judgment, and acting based on the available information.
In Summary
There are various complementary skills managers should have in order to manage their teams and departments effectively. These skills can help foster greater job satisfaction through motivation and engagement, strengthening bonds between employees and their colleagues.
By applying the skills from this guide to management practices, managers can transform their workforce into teams of A-players.