What is an attrition rate?
The employee attrition rate determines the reduction of the workforce due to a variety of factors, from retirement and resignations to sickness and promotions.
Sometimes referred to as the “churn rate”, the attrition rate can be easily measured and tracked over time. This allows companies to view their percentage of attrition and gain insights into employee satisfaction and employee retention.
What is the importance of the rate of attrition?
Monitoring attrition rates and understanding the root causes that drive the numbers is crucial for understanding how well the company is retaining the best talent. These rates not only show how many employees have left the organisation within a given period of time but what the reasons were for leaving.
From this data, business leaders can better adopt strategies to retain employees, addressing workplace well-being, motivation, engagement, and personal development in a variety of ways. This could mean working more closely with employees to ensure their personal and professional goals are aligned with the company or creating a better company culture that emphasises employee recognition.

The difference between turnover and attrition rate
It’s not uncommon for people to use the expressions “attrition rate” and “turnover” interchangeably. But while both terms refer to employees leaving the company, there is an important distinction to bear in mind.
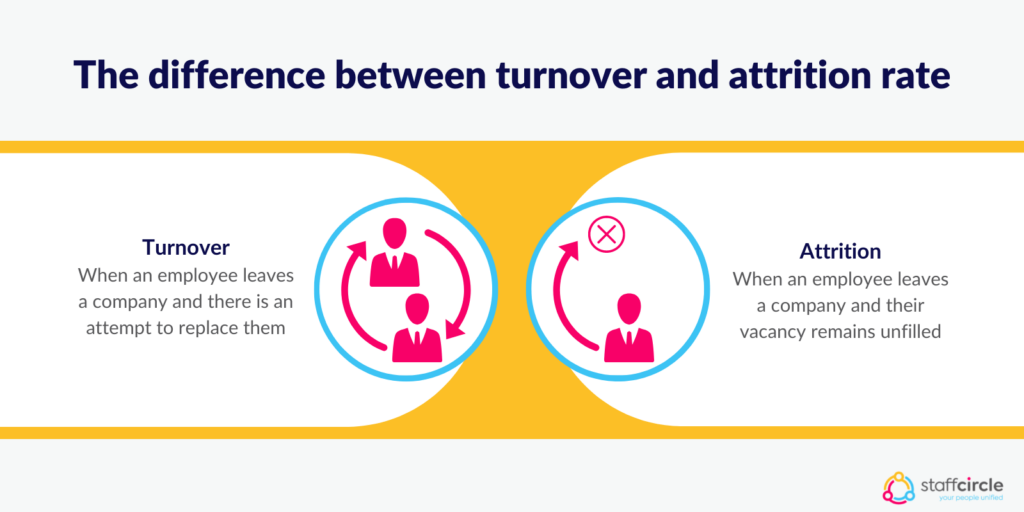
When an employee leaves the company and there is an attempt to replace the lost employee, this is known as turnover. When an employee leaves the company and their vacancy remains unfilled, this is an example of attrition.
The different attrition rates
There are several factors that influence a company’s attrition rates. Let’s take a look at these in more detail.
Voluntary attrition
Voluntary attrition occurs when an employee chooses to leave the company, whether due to taking on a new role in a different company, taking a career break or focusing on personal matters.
A report from Gallup, The ‘Great Resignation’ is Really The ‘Great Discontent, outlines how voluntary attrition rates are increasing due to employees actively seeking work elsewhere. One of the driving factors explored is the lack of engagement, with low engagement teams losing staff anywhere between 18% and 48% higher than engaged teams.
The article concludes with some thoughts on how business leaders can work to reduce voluntary attrition:
“Reversing the tide in an organization requires managers who care, who engage, and who give workers a sense of purpose, inspiration and motivation to perform. Such managers give people reason to stay.”
Involuntary attrition rate
When the company itself ends a member of staff’s employment, this loss of a member of staff contributes to the involuntary attrition rate. Typically, involuntary attrition occurs when the role in question is no longer needed by the organisation since attrition rates are associated with instances when the position is not filled once the employee exits.
Demographic specific attrition
Demographic-specific attrition refers to instances when a group of people leaves the organisation at the same time, with demographic characteristics such as gender, ethnicity, or age characterising the group.
This can sometimes be a cause for concern for business leaders, as demographic-based groups leaving the company en masse could mean there are inherent flaws in the company’s culture and diversity awareness.
Internal attrition rate
When an employee moves from one specific role on a team to another team or department, this influences the internal attrition rate. While many of the other forms of attrition need to be taken seriously and addressed, internal attrition can often be a positive event, for example when a member of staff is promoted to another role within the company.
Company attrition rate
The company attrition rate is the overall level of attrition experienced throughout the entire organisation. This encompasses all teams and departments and is expressed as a total percentage. A company attrition rate of less than 10% is typically considered to be desirable, although this can vary depending on the industry or sector.
How to calculate attrition rates
Calculating your company’s attrition rates can be easily done by following these simple steps. The formula you can use to calculate the attrition rate is as follows:
Attrition rate (%) = (number of leavers / number of employees) x 100
After choosing the period of time you wish to assess, divide the number of employees who have left the company by your average number of employees over the same period of time.
Once you’ve done this, take the divided amount and multiply it by 100.

As an example, if your company began with 100 employees and over the designated period of time 25 employees left the company and there were 5 new hires, this will leave 80 employees at the end of the period of time.
From this, you can calculate the average number of employees for the year:
(100+80) / 2 = 90
You can then calculate the percentage attrition rate as follows:
(20 / 90) x 100 = 22.2%
The higher the percentage, the more frequently employees are leaving the company. A lower rate indicates a stronger level of employee retention.

What causes attrition?
There is a range of factors that influence a company’s rate of attrition. These include:
Personal reasons
There is all manner of personal reasons that could lead a member of staff to leave the company. Relocating so that a partner can work another job, taking the time to help look after a loved one, or dealing with other personal issues can all play a role in attrition.
There are also personal reasons for leaving a company that are within the scope of business leaders to help reduce, for example:
- Incompatible workplace culture. Businesses with ill-defined and poorly framed workplace cultures can lead employees to seek work elsewhere. Toxic work environments can be particularly prone to high rates of attrition, as employees feel they would be a better fit seeking employment in a company with a clearer work ethic.
- Low levels of employee well-being. While some businesses ensure that physical and mental health and well-being is a top priority, others fail to appreciate why well-being is important, neglecting their responsibilities to look after their staff. Consequently, these employees can potentially suffer from deteriorating health and will seek new opportunities to move to a company in which they can thrive.
- Stress due to poor management and mismanagement. It goes without saying that stress can play a large role in an employee’s decision to vacate their role. If they lack the necessary support to accomplish their goals and manage their workload, the stress this brings can be enough to lead them to quit.
- The inability to advance within the company. Employees who feel as if they are going to be stuck in their current role for the foreseeable future – especially if that role is unfulfilling – will jump ship at the first sign of a better opportunity. Career advancement should be an integral aspect of any employee’s conversations with team leaders and managers.
Retirement age
Attrition through the retirement process is inevitable when employees reach their designated retirement age. One of the main causes of attrition, retirement is something businesses can plan for in advance, deciding whether or not to assign a replacement (in which case it would count as turnover), or leave the vacancy empty and distribute the retiree’s tasks among the remaining workers.
Career Promotion
Career promotion is an example of so-called “positive attrition” since the employee has left their role but remains within the company’s structure and on the payroll. Often, this occurs whenever a company has a good system in place to handle succession planning, giving existing employees the opportunity to develop their skills, progress within the company and enjoy promotions that further their careers.
Redundancy
Redundancy is another key factor around the concept of attrition that directly relates to the concept of the leaving employee’s role not being filled in their absence. When companies downsize or otherwise seek to reshuffle their workforce, employees may lose their jobs.
Termination
Employee termination occurs whenever an employee fails to live up to their role and responsibilities or commits a serious violation of company policy. Consistently failing to deliver expected results, excessive time off from work without a justification, and abuse or insubordination can all lead to termination that affects the company’s overall attrition rates.
What is the effect of having high attrition rates?
While there are exceptional circumstances where high attrition rates don’t have negative associations, attrition rates can impact your business in a variety of ways.
These include:
- Lowering employee morale. If employees see their colleagues leaving the company on a regular basis for negative reasons, they may lose confidence in their employer’s ability to keep staff satisfied.
- Overworked employees. If roles vacated by employees are not filled, this can sometimes mean that elements of the roles and responsibilities are passed on to others. Adding additional work to other staff can lead to overwork, potential burnout, and unwanted stress.
- Deterioration in the product or service the company offers. If attrition results in key staff no longer working at the company – or simply not enough staff to get everything done – project deadlines and overall company performance can deteriorate. This can result in reductions in revenue that could potentially lead to further workplace attrition.
How to reduce attrition rates
If your business is experiencing higher than desired attrition rates, there are several steps that can be taken to address this. Here are some steps worth considering to help reduce attrition rates.
Using technology to reduce attrition
The Forbes article on how businesses can use technology to reduce turnover outlines the core issue facing businesses in the present era. The article states:
“Now more than ever, employees are leaving organizations at record rates, creating an excess of vacant positions in the job market. Companies are experiencing difficulties retaining or recapturing workers. Human resource departments make great efforts to engage employees, offering a more exciting experience to boost recruitment and retention rates and improve the bottom line.”
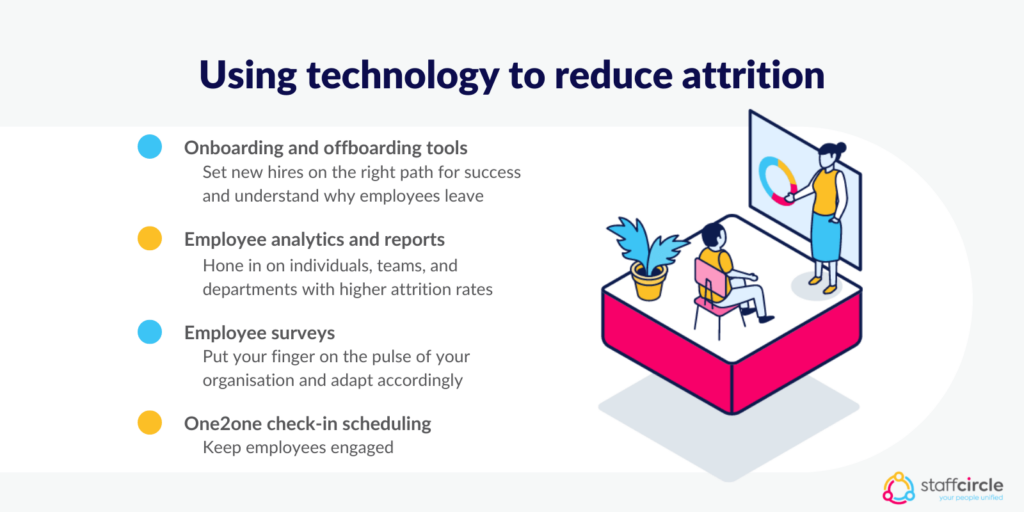
Performance management software offers HR professionals and managers a variety of tools that can be used to reduce attrition. These tools include.
- Onboarding and offboarding tools to help set new hires on the right path for success, and better understand the motives behind employees who leave the company.
- Employee analytics and reports help business leaders hone in on individuals, teams, and departments with higher attrition rates so that solutions can be determined.
- Employee surveys help leaders put their fingers on the pulse of the organisation and adapt accordingly.
- One2one check-in scheduling and feedback keeps employees engaged with their direct reports on a day-to-day basis.
Maintain a good and positive workforce culture
Companies with the lowest rates of attrition and turnover are those which cherish their employees and create a work environment where their success is desirable. Culture feedback mechanisms can be put in place to help business leaders craft better core values and set a mission statement that brings employees together, improving employee retention.
Evaluate the goals of your employees and what motivates them
Employees who are engaged with their work and feel a part of the company are more likely to be motivated. Understanding the impact of performance management on employee motivation is essential to keeping attrition rates down.
This means fostering leadership that engages in continuous conversations about career development with their staff and setting appropriate goals to help with this aim. Instituting awards and recognition programs is another effective method for keeping staff motivated while also dealing with health and well-being.
Can high attrition rates be a positive?
While high attrition rates are typically associated with negative company performance, there are exceptional circumstances. High rates of involuntary attrition could mean the company is shedding employees who are no longer bringing value to the organisation and draining time and resources.
It can also be a reflection of the injection of better talent, with new blood invigorating the company’s overall performance with fresh ideas and new approaches. In purely financial terms, high attrition often means that costs are lowered through the removal of employees who are no longer required to achieve business goals.
Summary
Calculating your company’s attrition rate is essential for understanding levels of employee engagement, motivation, and the company’s overall retention. If attrition rates are high, this opens the door to a variety of ways to improve employee retention at work, creating a happier, more productive workforce.