The Bradford Factor is a tried and tested HR tool used to help understand how frequent sickness patterns are impacting the company’s performance. Read on to discover how you can implement it to gain insights into absence patterns, and what additional methods you need to avoid unfair outcomes.
What is the Bradford Factor?
One of the pillars of an effective performance management strategy is the monitoring of absence and sickness patterns. By using the Bradford Factor calculator, employers can gain insights into how frequently members of staff take time off for sickness.
This data, combined with other methods of analysis and feedback, can be used to help those employees who are struggling with attendance. It can also be used to identify patterns of absence within teams and departments, setting benchmarks for absence rates throughout the company.
How does the Bradford Factor work?
One of the biggest hidden costs to running a company comes from unnecessary time off. A study in 2019 by Viking discovered that UK businesses lost £5.6 billion that year due to workers who lied about requiring a sick day.
The report found that 38% of sick days taken were not actually for illness. This comprised a total of 51.9 million sick days which were fake, leading to huge losses for businesses around the country.
The Bradford Factor score gives employers valuable insights into employee absences. Identifying employees who take frequent sickness absences can help managers address a range of performance issues.
Since frequent absences cause the most disruptions, managers and HR leaders can use the Bradford Factor scores to determine which employees need the most attention. They can work with the employees with the highest scores to help address their number of absences.

How are Bradford factor scores calculated?
Calculating a Bradford Factor score is easy to do, and can be achieved through the relevant HR software. The basic equation of the Bradford Factor calculator appears like this:
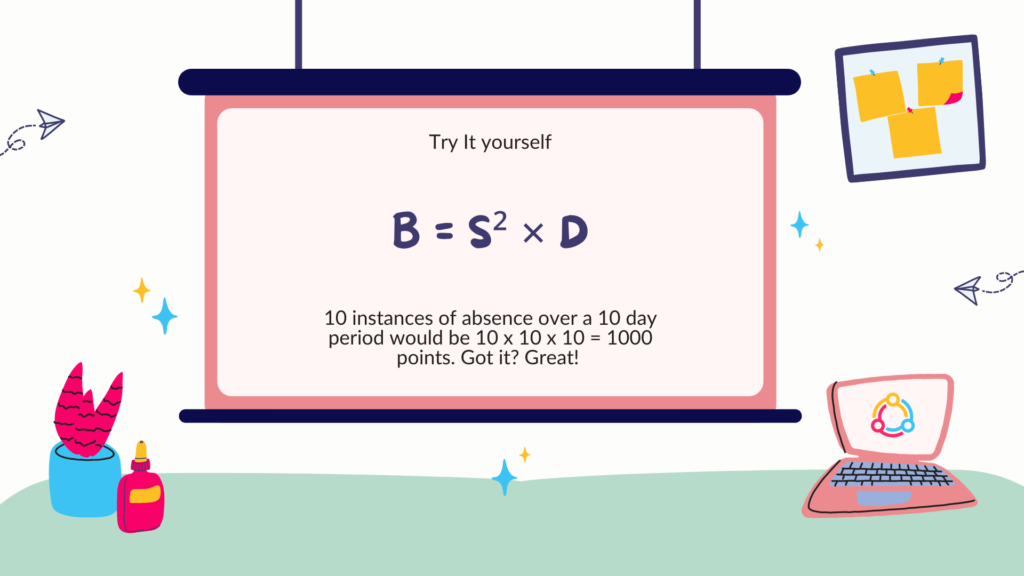
B = S² × D
These letters stand for:
- B represents the Bradford Factor
- S represents the spells (or instances) of an individual’s absence over a determined period of time
- D represents the total number of absence days over the same period of time
For example, 10 instances of absence over a 10 day period would be 10 x 10 x 10 = 1000 points.
This formula makes sure that employees who take frequent if shorter spells of absence over a period of time will have a higher Bradford Factor score than those who take long but infrequent absences.
History of Bradford Factor score
The exact origins of the Bradford Factor remain unclear to this day. It takes its name from Bradford University School of Management, based on the results of a research team based there in the 1980s.
In fact, Bradford University has stated that no such research has been conducted there, leaving people to speculate as to its real origins. The Financial Times stated in an article:
“HR folklore sources it to a pharmaceutical company in the 1980s whose managers attended a seminar at the Bradford University School of Management (Bradford University didn’t reply to my questions about it).”
Since its creation, a number of other methods have been adopted to help assess absence patterns. For example:
Lost Time Rate
Using the Lost Time Rate allows you to work out the percentage of total time lost on account of absence. The number of hours of absence are divided by the total possible working hours to give this percentage.
Absence Frequency Rate
The absence frequency rate calculates all the individual instances of absence occurring within an organisation. This figure is arrived at by dividing the total absences by the total number of employees.
The Consolidated Approach
The consolidated approach combines both of the above methods to give business leaders a broader insight into absence patterns. This gives a clearer – but still imperfect – picture of how sickness affects the company.

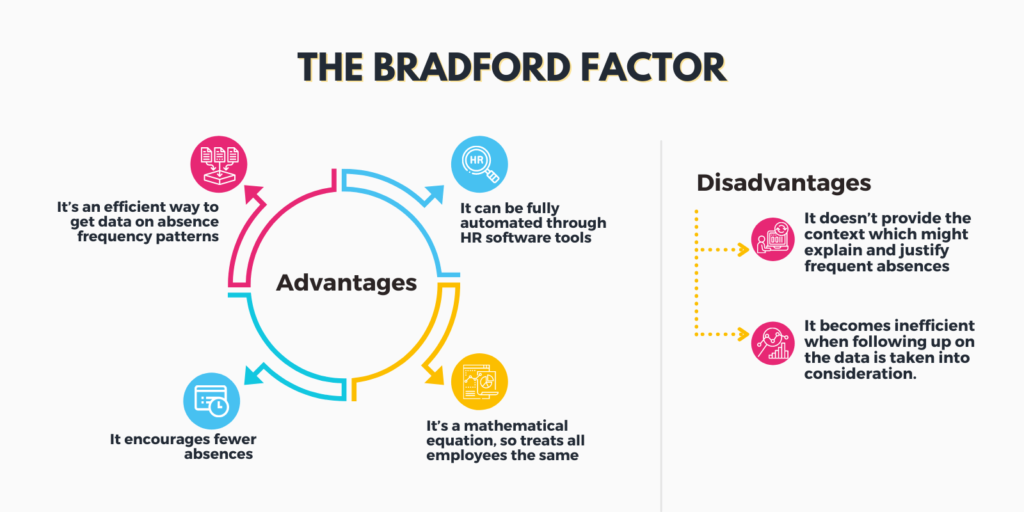
The advantages of the Bradford Factor
As with many data-gathering methods, the Bradford Factor has its pros and cons. Here are some of the advantages you can gain through applying the Bradford Factor score to analyse employee absences:
- It’s an efficient way to get data on absence frequency patterns
- It can be fully automated through HR software tools
- It’s a mathematical equation, so treats all employees the same
- It encourages fewer absences and gets employees to consider how frequent absences may affect performance
The disadvantages of the Bradford Factor
There are several disadvantages to the Bradford Factor which warrant consideration. These include:
- By treating all employees the same in its analysis, the Bradford Factor fails to treat people fairly. It doesn’t provide the context which might explain and justify frequent absences, such as ongoing health issues which require regular hospital visits
- It becomes inefficient when following up on the data is taken into consideration. While the raw data itself can be helpful to identify patterns, the reasons behind those patterns requires additional time and effort to discover
How useful are Bradford factor scores?

Most organisations use the Bradford Factor as part of their overall strategy of assessing sickness rates. It’s a common feature in many HR software suites, while its ability to automate reports makes it simple to use.
However, in order to make the most of the Bradford Factor, other measures need to be taken. For example, long-term illnesses and disabilities are not taken into consideration when using this formula. To account for this, HR leaders should make sure they include these factors when analysing sickness in the workforce.

Using continuous feedback
Medical conditions are often included in an employee’s personal profile. But there are other circumstances that may lead to frequent sickness absences which might go under the radar. Stress, anxiety, or an illness in the family can all affect attendance without team leaders or managers being aware of the problem.
By scheduling and conducting regular one2one check-ins, employers can make sure continuous feedback picks up these issues. Managers can include questions about mental health and well-being as a matter of course so that employees who are taking frequent sick days for legitimate reasons aren’t unfairly disciplined because of Bradford Factor scores.
Frequently asked questions

How do you calculate the Bradford Factor?
Using the Bradford Factor calculator to determine your employees’ rates of absence is easy. Simply multiply the total number of instances of absences by itself (e.g. 7 x 7), then multiply this number by the total number of absence days.
For a more detailed explanation, head to the top of this article.
Is Bradford Factor legal?
The Bradford Factor sits within the concept of guidelines rather than rules, although it is legal to take action against employees who are repeatedly absent from work. While the score given is a useful guide and can be used as a benchmark for trigger points, all factors need to be considered before taking any action against an employee.
Is the Bradford Factor effective?
The Bradford factor gives employers a clear data set that they can use for the assessment of sickness. However, it is only fully effective when used alongside other methods to determine whether or not frequent absences are justified or not.
How many sick days are acceptable in a year
While there are no firm guidelines on how many sickness absences an employee can have each year, the national average in the UK as of 2018 is 4.4, according to the Office of National Statistics.
Businesses are free to establish their own threshold for absences, but should always take into account mitigating circumstances for employees who pass this figure.